The Nigerian retail industry analysis reveals a complex marketplace where understanding competitive forces determines success. Nigeria’s retail sector, valued at over $13.2 billion, continues growing despite economic pressures. This growth creates opportunities for businesses ready to understand market dynamics.
At Novatia Consulting, we help businesses apply strategic frameworks like Porter’s Five Forces to make informed decisions. This proven model examines five key competitive forces that shape industry profitability and attractiveness. For Nigerian retailers facing inflation, currency volatility, and infrastructure challenges, this framework provides clarity.
This article examines how Porter’s Five Forces applies to Nigeria’s retail landscape. We’ll explore competitive rivalry, buyer power, supplier influence, new entrant threats, and substitute products. Each section offers practical insights to help your business thrive.
Understanding the Nigerian Retail Industry Analysis Landscape
Nigeria’s retail sector stands as Africa’s most dynamic marketplace. With over 230 million people and growing urbanization, the country presents immense potential. However, success requires understanding unique local characteristics.
The Nigerian retail industry analysis shows traditional trade dominates 90% of transactions. Small shops, market stalls, and street vendors form the backbone of distribution. Yet modern retail formats are expanding rapidly in urban centers like Lagos and Abuja.
Recent economic reforms have reshaped operations. The removal of fuel subsidies in 2024 increased operational costs significantly. Currency depreciation affects import-dependent retailers. Inflation erodes consumer purchasing power.
Despite these challenges, retail remains Nigeria’s second-largest GDP contributor. The sector employs millions and continues attracting investment. Understanding this landscape helps businesses position themselves effectively.
Technology increasingly influences Nigerian retail industry analysis. Mobile payments, digital platforms, and data analytics transform how retailers operate. Internet penetration exceeds 70%, driving e-commerce growth.
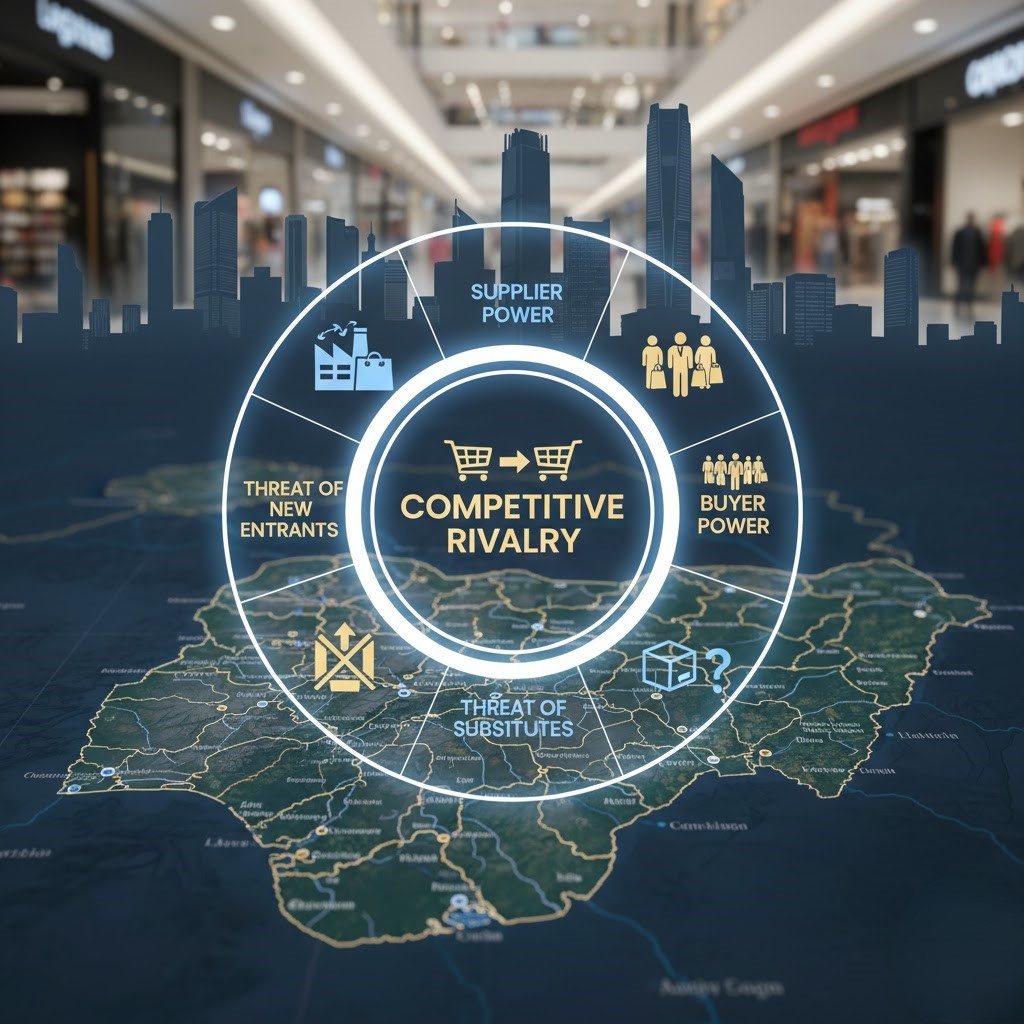
How Porter’s Five Forces Framework Transforms Retail Market Competition Nigeria
Porter’s Five Forces model provides a comprehensive lens for analyzing retail market competition Nigeria. Developed by Michael Porter, this framework identifies five forces determining industry profitability.
The model goes beyond simple competitor analysis. It examines the broader competitive environment including suppliers, buyers, potential entrants, and substitutes. This holistic view helps businesses understand where threats and opportunities exist.
For Nigerian retailers, this framework proves particularly valuable. The market’s complexity demands structured analysis. Informal channels, diverse consumer preferences, and regulatory considerations create multiple pressure points.
At Novatia Consulting, we’ve seen how applying this model transforms decision-making. Businesses gain clarity on where to compete and how to position themselves. Strategic choices become data-driven rather than intuition-based.
The framework also highlights interconnections between forces. Strong buyer power might intensify competitive rivalry. High supplier bargaining strength could increase substitute threats. Understanding these relationships creates strategic advantage.
In retail market competition Nigeria, Porter’s model remains highly relevant. While created decades ago, its principles adapt well to emerging markets. The framework’s flexibility allows customization for local contexts.
Competitive Rivalry in Nigeria’s Retail Sector: What Businesses Must Know
Competitive rivalry represents the most visible force in retail market competition Nigeria. The sector experiences intense competition across all formats.
Traditional retailers compete fiercely on price and convenience. With thousands of small shops in every neighborhood, competition stays hyperlocal. Margins remain thin as vendors undercut each other.
Modern retail formats face different competitive dynamics. Supermarket chains like Shoprite and Spar compete through quality, variety, and shopping experience. However, they also compete with traditional markets offering lower prices.
E-commerce platforms add another competitive layer. Companies like Jumia and Konga compete with both traditional and modern retailers. They offer convenience and variety that physical stores struggle to match.
Product differentiation proves challenging in Nigerian retail industry analysis. Many retailers stock similar products. Building brand loyalty becomes difficult when consumers prioritize price over brand.
The competitive intensity increases during economic downturns. When consumers reduce spending, retailers fight harder for shrinking wallets. Promotional activities intensify, further squeezing margins.
Nevertheless, opportunities exist for differentiation. Retailers focusing on customer service, local products, or niche markets can reduce direct competition. Understanding your competitive position within Porter’s framework helps identify these opportunities.
Buyer Power and Consumer Influence in Nigerian Retail Industry Analysis
Buyer power in Nigerian retail industry analysis ranks among the strongest forces. Consumers wield significant influence through their choices and price sensitivity.
Price consciousness dominates consumer behavior. With inflation affecting purchasing power, shoppers constantly seek better deals. They readily switch between retailers for minor price differences.
The abundance of alternatives strengthens buyer power. In any Nigerian city, consumers access dozens of shopping options within walking distance. Traditional markets, convenience stores, and supermarkets all compete for attention.
Brand loyalty remains relatively low in many retail categories. While consumers show loyalty for certain premium products, most shopping decisions prioritize value. This behavior increases buyer bargaining power.
However, buyer power varies by product category. For basic necessities like food and household goods, price sensitivity peaks. For premium items and electronics, brand and quality considerations reduce pure price competition.
Digital platforms amplify buyer power. Online shoppers easily compare prices across retailers. Reviews and ratings influence purchasing decisions. This transparency forces retailers to remain competitive.
Retailers can reduce buyer power through differentiation. Offering unique products, superior service, or loyalty programs builds switching costs. Creating emotional connections with customers reduces pure price competition.
At Novatia Consulting, we help retailers understand their specific buyer segments. Different customer groups exhibit varying levels of price sensitivity. Targeting less price-sensitive segments can improve profitability.
Supplier Bargaining Strength: A Critical Factor in Retail Market Competition Nigeria
Supplier power presents moderate to strong influence in retail market competition Nigeria. This force varies significantly across product categories and retailer types.
Large retailers enjoy stronger negotiating positions. Chains like Shoprite can demand favorable terms due to volume purchases. They can switch suppliers relatively easily, reducing supplier power.
Small traditional retailers face opposite dynamics. Limited purchasing power means accepting supplier terms. These retailers often rely on local wholesalers and distributors who control access to products.
Import dependency increases supplier power in certain categories. Retailers stocking imported goods face currency risk and supply chain vulnerabilities. International suppliers may have few local competitors.
The Nigerian retail industry analysis shows growing emphasis on local sourcing. This strategy reduces currency exposure and supports domestic producers. However, local suppliers sometimes lack capacity or consistency.
Quality differentiation strengthens certain suppliers. Brands with strong consumer recognition can demand premium placement and terms. Retailers need these products to attract customers.
Supply chain disruptions amplify supplier power. Poor infrastructure, security concerns, and logistical challenges give suppliers leverage. Retailers may accept unfavorable terms to ensure consistent supply.
Forward integration by suppliers creates additional pressure. Some manufacturers now sell directly to consumers through their own stores or online platforms. This move intensifies competition and shifts power dynamics.
Retailers can mitigate supplier power through diversification. Building relationships with multiple suppliers reduces dependency. Investing in local supplier development creates long-term partnerships and stability.
Threat of New Entrants Reshaping Porter’s Five Forces Retail Dynamics
The threat of new entrants in Porter’s Five Forces retail framework shows mixed intensity in Nigeria. Barriers to entry vary dramatically across retail formats.
Traditional retail faces extremely low entry barriers. Anyone can set up a small shop or market stall with minimal capital. This accessibility explains why informal retail dominates Nigerian retail industry analysis.
However, modern retail presents substantial barriers. Establishing supermarket chains requires significant capital investment. Real estate costs in prime locations remain high. Building supply chains and distribution networks demands resources and expertise.
Regulatory requirements create moderate barriers. Business registration, tax compliance, and permits add complexity. Foreign retailers face additional restrictions and local partnership requirements.
Brand recognition serves as a significant barrier. Established retailers benefit from customer trust and loyalty. New entrants must invest heavily in marketing to build awareness.
E-commerce reduces some traditional barriers while creating new ones. Online platforms lower physical infrastructure requirements. However, last-mile delivery challenges and payment system complexities create different obstacles.
Technology integration increasingly becomes a barrier. Modern retailers need point-of-sale systems, inventory management software, and data analytics capabilities. These requirements demand expertise and investment.
Despite barriers, new entrants keep emerging in retail market competition Nigeria. International retailers see growth potential. Local entrepreneurs identify niche opportunities. This constant entry maintains competitive pressure.
Existing retailers must continually innovate to maintain advantages. Building strong customer relationships, developing efficient operations, and creating unique value propositions help defend market position.
Substitute Products and Services: Challenges Facing Nigerian Retail Industry Analysis
The threat of substitutes represents a growing concern in Nigerian retail industry analysis. Multiple factors drive substitution patterns affecting traditional retail formats.
E-commerce serves as the primary substitute for physical retail. Online shopping offers convenience and variety that brick-and-mortar stores struggle to match. This shift accelerated during the pandemic and continues growing.
Direct-to-consumer brands bypass traditional retail entirely. Manufacturers sell through their own channels, using social media and websites. This approach threatens retailers’ role as intermediaries.
Informal channels provide substitution at the lower end. Street vendors and market traders offer ultra-convenience and flexible payment terms. For budget-conscious consumers, these alternatives remain attractive.
Service-based alternatives also emerge. Subscription boxes, meal delivery services, and personal shopping services compete with traditional grocery shopping. These models appeal to time-pressed urban consumers.
The threat varies significantly across product categories. Commodity items face higher substitution risk. Specialty products with limited alternatives face lower threats.
Technology enables new substitution patterns in retail market competition Nigeria. Mobile apps connect consumers with vendors directly. Social commerce through WhatsApp and Instagram creates alternative shopping channels.
However, substitution faces barriers in Nigeria. Infrastructure limitations constrain e-commerce growth. Payment system challenges reduce online shopping adoption. Product authenticity concerns make consumers prefer physical inspection.
Retailers can address substitution threats through adaptation. Offering omnichannel experiences, improving delivery services, and enhancing in-store experiences reduce substitute appeal.
At Novatia Consulting, we help retailers identify substitution risks specific to their markets. Understanding these threats early allows proactive response strategies.
How Novatia Consulting Applies Porter’s Five Forces Retail Framework for Strategic Success
At Novatia Consulting, we believe Porter’s Five Forces retail analysis provides the foundation for sound strategy. Our approach goes beyond theoretical application to practical implementation.
We start by conducting comprehensive industry assessments. This process involves analyzing all five forces within your specific retail context. We examine quantitative data and qualitative insights to build complete pictures.
Our Nigerian retail industry analysis methodology includes competitive benchmarking. We compare your position against key competitors across multiple dimensions. This comparison reveals relative strengths and weaknesses.
We help clients identify strategic opportunities within each force. Weak supplier power might suggest vertical integration opportunities. Strong buyer power could indicate need for differentiation strategies.
Our recommendations balance theoretical rigor with practical feasibility. We consider your resources, capabilities, and risk tolerance. Strategic options must be both theoretically sound and operationally achievable.
Technology plays a central role in our analysis approach. We use data analytics to quantify force intensity. Market research provides insights into consumer behavior and preferences.
Implementation support distinguishes Novatia Consulting’s services. We don’t just deliver reports. We work alongside management teams to execute strategies. Change management, training, and ongoing support ensure success.
We also provide regular reassessments. Market conditions change, especially in dynamic retail market competition Nigeria. Periodic reviews keep strategies aligned with evolving realities.
Our client success stories demonstrate Porter’s framework effectiveness. Retailers who understand competitive forces make better decisions. They allocate resources more efficiently and achieve sustainable competitive advantages.
E-Commerce vs Traditional Retail: Navigating Retail Market Competition Nigeria
The competition between e-commerce and traditional retail defines modern retail market competition Nigeria. Each format offers distinct advantages and faces unique challenges.
Traditional retail maintains dominance through physical presence and immediacy. Consumers can inspect products, take immediate possession, and avoid delivery delays. These advantages remain significant in Nigerian contexts.
Relationships drive traditional retail success. Shop owners know their customers personally. They offer credit, understand preferences, and provide personalized service. This human connection builds loyalty.
However, traditional retail faces serious challenges. Limited product variety constrains choice. Physical store locations limit accessibility. Operating hours restrict convenience.
E-commerce addresses these limitations effectively. Online platforms offer vast product selections. Shopping happens anytime, anywhere. Price comparisons become effortless.
Infrastructure constraints limit e-commerce growth in Nigerian retail industry analysis. Poor addresses complicate deliveries. Limited payment options create friction. Internet access remains inconsistent outside major cities.
Trust issues also affect online shopping adoption. Concerns about product quality, counterfeit goods, and fraud deter consumers. Many Nigerians prefer seeing products before buying.
The future likely involves hybrid models. Successful retailers will blend physical and digital channels. Click-and-collect services, online ordering with in-store pickup, and showrooming represent this convergence.
Mobile commerce drives Nigerian e-commerce growth. Smartphones enable shopping without computers. Mobile money solutions address payment challenges. Social commerce through WhatsApp and Instagram thrives.
Traditional retailers can compete by adopting technology. Simple WhatsApp ordering, local delivery services, and digital payment acceptance help bridge the gap.
At Novatia Consulting, we help retailers develop omnichannel strategies. Neither format represents the complete future. Success requires understanding when each model works best.
Infrastructure and Regulatory Barriers in Nigerian Retail Industry Analysis
Infrastructure challenges significantly impact Nigerian retail industry analysis and competitive dynamics. These systemic issues affect all market participants but impact businesses differently.
Transportation infrastructure remains inadequate across much of Nigeria. Poor road conditions increase logistics costs and delivery times. This situation favors retailers with strong distribution networks and local sourcing capabilities.
Power supply unreliability forces retailers to invest in backup generators. This requirement significantly increases operational costs. Small retailers particularly struggle with energy expenses.
The addressing system’s absence complicates deliveries. Street names and house numbers often don’t exist in many areas. This problem especially constrains e-commerce growth.
Payment infrastructure continues improving but challenges persist. Cash remains dominant despite growing digital adoption. Retailers must manage cash security risks while developing alternative payment acceptance.
Regulatory complexity adds another layer of difficulty in retail market competition Nigeria. Multiple agencies oversee different retail aspects. Compliance requires navigating federal, state, and local requirements.
Licensing and permit processes often prove opaque and time-consuming. Bureaucratic delays can stall store openings and expansions. These hurdles favor established players with government relationships.
Import regulations affect product availability and pricing. Restricted items, customs delays, and tariff structures all influence retail operations. Retailers must stay current with frequently changing policies.
Consumer protection regulations continue evolving. While necessary for market integrity, compliance requires investment in systems and training. Smaller retailers may lack resources for full compliance.
Security concerns affect retail location decisions and operations. Some areas remain challenging for formal retail due to safety issues. Security costs reduce profitability.
Despite these challenges, infrastructure gradually improves. Government initiatives target road construction, power generation, and digital infrastructure. Patient retailers positioned for long-term growth can benefit.
Novatia Consulting helps clients navigate these barriers strategically. Understanding infrastructure constraints allows better location selection, supply chain design, and operational planning.
Local and International Players: Understanding Competitive Intensity Through Porter’s Five Forces Retail

The mix of local and international players creates unique dynamics in retail market competition Nigeria. Each group brings different strengths, weaknesses, and strategic approaches.
International retailers typically offer superior systems and processes. Companies like Shoprite import best practices from their home markets. They deliver consistent quality, variety, and shopping experiences.
These players also access international supply chains and capital. They can weather economic storms better than local competitors. Brand recognition from their home markets sometimes transfers to Nigerian consumers.
However, international players face significant challenges in Nigerian retail industry analysis. Cultural differences affect product assortment and marketing. Management expatriates may misunderstand local preferences.
Regulatory restrictions limit foreign ownership in certain sectors. Partnership requirements with local investors create governance complexities. Repatriation of profits faces currency controls.
Local retailers possess deep market knowledge. They understand customer preferences, seasonal patterns, and community dynamics. These insights create competitive advantages international players struggle to replicate.
Local players also maintain better relationships with suppliers and government officials. These connections smooth operations and create favorable terms. Their flexibility allows quick adaptation to market changes.
Small local retailers benefit from low cost structures. Operating from modest locations with family labor keeps expenses minimal. They can profitably serve market segments uneconomical for large chains.
However, local players often lack capital for expansion. Limited access to financing constrains growth. They may also lack management expertise and systems for scaling operations.
The competitive intensity increases as these groups interact. International players bring competition that forces local retailers to improve. Local players exploit weaknesses in international competitors’ approaches.
Some local retailers partner with international brands through franchising. This model combines local market knowledge with international systems and brands. Success stories include various quick-service restaurant franchises.
At Novatia Consulting, we help both local and international clients understand competitive positioning. Success requires playing to your strengths while addressing weaknesses.
Consumer Behavior Trends Driving Retail Market Competition Nigeria

Understanding consumer behavior proves essential for success in Nigerian retail industry analysis. Several key trends shape purchasing decisions and competitive dynamics.
Price sensitivity dominates consumer behavior across most categories. Economic pressures make shoppers extremely value-conscious. They compare prices actively and switch retailers for better deals.
However, quality concerns also influence decisions. Rising middle-class consumers increasingly prioritize product quality and authenticity. They pay premiums for trusted brands.
Convenience gains importance, especially among urban professionals. Time-pressed consumers value retailers offering easy access, fast checkout, and delivery options. This trend drives modern format growth.
Trust plays an outsized role in retail market competition Nigeria. Consumers prefer retailers with reputations for honest dealing. Previous positive experiences create loyalty that price advantages alone may not overcome.
Social recommendations heavily influence purchasing decisions. Family, friends, and community opinions matter more than advertising. Word-of-mouth marketing proves extremely powerful.
The youth demographic reshapes retail landscapes. Nigeria’s median age stays under 20 years. Young consumers embrace technology, seek modern experiences, and show openness to new brands.
Payment flexibility affects shopping choices. Many consumers lack consistent income streams. Retailers offering credit or flexible payment arrangements gain competitive advantages.
Sustainability awareness slowly grows among educated urban consumers. Some shoppers now consider environmental and social impacts. Local sourcing and ethical business practices increasingly influence choices.
Mobile phone usage transforms shopping behavior. Consumers research products online before buying in stores. Social media platforms become shopping channels. Mobile payments grow steadily.
Cultural and religious factors shape retail patterns. Seasonal spending spikes around holidays like Christmas, Eid, and traditional festivals. Product preferences reflect cultural values and norms.
At Novatia Consulting, we help retailers align strategies with these behavioral trends. Understanding your target customers deeply allows more effective positioning and marketing.
Strategic Positioning: Leveraging Porter’s Five Forces Retail for Growth
Strategic positioning using Porter’s Five Forces retail framework enables sustainable competitive advantage. The key lies in understanding your unique position within competitive forces.
Cost leadership represents one positioning strategy. Retailers achieving lowest cost structures can offer competitive prices while maintaining margins. This approach requires operational excellence and scale.
However, cost leadership proves challenging in Nigerian retail industry analysis. Infrastructure costs and supply chain inefficiencies create baseline expenses affecting everyone. Pure cost competition often leads to destructive margin erosion.
Differentiation offers alternative positioning. Retailers creating unique value propositions can command premium prices. Superior service, exclusive products, or exceptional experiences justify higher costs.
Focus strategies target specific market segments. Rather than competing broadly, focused retailers serve niche markets exceptionally well. This approach works particularly well for smaller players.
Geographic focus proves effective in retail market competition Nigeria. Mastering specific regions or neighborhoods allows deep customer understanding. Local dominance provides defensible positions against larger competitors.
Vertical integration represents another strategic option. Retailers controlling supply chains reduce supplier power while improving margins. Some Nigerian retailers now manufacture their own private label products.
Strategic partnerships can strengthen competitive position. Collaborating with complementary businesses creates value neither could achieve alone. These alliances might involve suppliers, technology providers, or even competitors.
Omnichannel strategies blend physical and digital retail strengths. Retailers offering seamless experiences across channels serve customer preferences better. This integration requires investment but creates competitive moats.
Timing also matters in strategic positioning. First movers in emerging segments can establish dominant positions. However, fast followers often learn from pioneer mistakes and execute better.
At Novatia Consulting, we help clients identify optimal positioning strategies. This process considers your resources, capabilities, market conditions, and competitive dynamics through Porter’s framework.
Technology Integration and Its Impact on Nigerian Retail Industry Analysis
Technology transforms Nigerian retail industry analysis and competitive dynamics. Digital tools reshape operations, customer experiences, and strategic possibilities.
Point-of-sale systems revolutionize inventory management. Real-time tracking prevents stockouts and reduces excess inventory. Data from these systems inform purchasing decisions and identify sales trends.
Customer relationship management platforms enable personalized marketing. Retailers can segment customers, track preferences, and deliver targeted promotions. This capability builds loyalty and increases purchase frequencies.
E-commerce platforms expand market reach beyond physical locations. Retailers access customers across Nigeria through online channels. This expansion changes competitive dynamics and growth trajectories.
Mobile payment systems address cash handling challenges in retail market competition Nigeria. Digital payments improve security, reduce theft risks, and provide transaction data. Adoption continues accelerating.
Data analytics provides competitive intelligence. Understanding sales patterns, customer behaviors, and market trends allows better decision-making. Predictive analytics forecast demand and optimize operations.
Social media platforms become marketing and sales channels. Instagram, Facebook, and WhatsApp enable direct customer engagement. Social commerce grows rapidly among tech-savvy Nigerian consumers.
Supply chain technology improves efficiency. Route optimization software reduces delivery costs. Supplier management systems streamline procurement. These improvements directly affect profitability.
Cloud computing reduces technology barriers. Small retailers access enterprise-grade systems without massive upfront investments. Subscription models make sophisticated tools affordable.
Artificial intelligence begins appearing in Nigerian retail. Chatbots handle customer service queries. Recommendation engines suggest products based on browsing history. These applications will expand.
However, technology adoption faces barriers. Initial investment costs deter some retailers. Skills gaps limit implementation effectiveness. Infrastructure constraints affect reliability.
At Novatia Consulting, we guide retailers through technology adoption journeys. Successful integration requires choosing appropriate tools, training staff, and changing processes systematically.
Future Outlook: Building Competitive Advantage in Retail Market Competition Nigeria with Novatia Consulting
The future of retail market competition Nigeria holds both challenges and opportunities. Understanding emerging trends allows proactive positioning for success.
Economic growth will continue driving retail expansion. Despite short-term volatility, Nigeria’s long-term trajectory favors increased consumer spending. Population growth and urbanization support market development.
Modern retail formats will gain market share gradually. Traditional trade will remain important but its dominance will slowly decline. The transition creates opportunities for hybrid models.
E-commerce adoption will accelerate as infrastructure improves. Better logistics, payment systems, and internet access remove current barriers. Retailers must develop digital capabilities now.
Sustainability will increasingly influence competitive positioning in Nigerian retail industry analysis. Consumers and regulators will demand environmental responsibility. Forward-thinking retailers will lead this transition.
Consolidation may reshape competitive landscapes. Smaller retailers will face pressure to join groups or networks. Some will exit while others find successful niches.
Technology will continue disrupting traditional models. Artificial intelligence, blockchain, and Internet of Things applications will create new possibilities. Early adopters will gain significant advantages.
Regulatory environments will evolve. Government policies on retail, competition, and consumer protection will shape industry structure. Successful retailers will influence policy while adapting to changes.
Regional integration may expand opportunities. African Continental Free Trade Area implementation could ease cross-border retail operations. Nigerian retailers might expand into neighboring markets.
Consumer preferences will keep evolving. Younger generations bring different expectations and behaviors. Retailers must stay attuned to changing demands.
At Novatia Consulting, we help clients prepare for these futures. Using Porter’s Five Forces retail framework, we identify strategic directions robust across multiple scenarios. Our approach balances current performance with future positioning.
Building competitive advantage requires understanding all five forces deeply. It demands honest assessment of your position and realistic appraisal of competitors. Success comes from making strategic choices aligned with your capabilities and market realities.
We partner with retailers at all stages. Whether you’re entering the market, expanding operations, or transforming existing businesses, we provide insights and support. Our experience across Nigerian retail industry analysis ensures practical, actionable recommendations.
The Nigerian retail sector offers tremendous opportunities for those who understand its dynamics. Porter’s Five Forces provides the analytical framework for this understanding. Combined with local expertise and strategic thinking, this framework enables sustainable competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Porter’s Five Forces apply to Nigerian retail industry analysis?
Porter’s Five Forces examines competitive rivalry, buyer power, supplier strength, threat of new entrants, and substitute products in Nigerian retail. This framework helps businesses understand market dynamics, identify strategic opportunities, and make informed decisions about positioning and growth in Nigeria’s complex retail environment.
What makes retail market competition Nigeria so intense?
Retail market competition Nigeria stays intense due to low entry barriers for traditional retail, high consumer price sensitivity, abundant shopping alternatives, and mix of local and international players. Economic pressures, infrastructure challenges, and rapid e-commerce growth add complexity, forcing retailers to constantly adapt strategies.
Why is buyer power so strong in Nigerian retail industry analysis?
Buyer power remains strong because Nigerian consumers are extremely price-sensitive, have numerous shopping alternatives within easy reach, show low brand loyalty for most categories, and readily switch retailers for better prices. Economic pressures amplify these behaviors, giving consumers significant influence over retailers.
How can small retailers compete against large chains in retail market competition Nigeria?
Small retailers can compete by offering personalized service, building strong community relationships, maintaining flexible credit arrangements, stocking locally-preferred products, and operating with lower overhead costs. Leveraging technology like mobile payments and social commerce also helps level the playing field.
What role does technology play in Porter’s Five Forces retail framework?
Technology reshapes all five forces by enabling e-commerce (new entrants), empowering consumers with information (buyer power), improving supply chain efficiency (supplier power), creating substitutes for physical retail, and intensifying competitive rivalry through data analytics, mobile commerce, and digital marketing capabilities.
How does infrastructure affect Nigerian retail industry analysis?
Infrastructure challenges increase logistics costs, create delivery barriers, limit store locations, and raise operational expenses through backup power requirements. These factors influence competitive positioning, favor established players with distribution networks, and constrain e-commerce growth while creating opportunities for innovative solutions.
Can international retailers succeed in retail market competition Nigeria?
International retailers can succeed by partnering with local experts, adapting product assortments to Nigerian preferences, investing in supply chain infrastructure, and building trust gradually. Success requires patience, understanding cultural nuances, and balancing global best practices with local market realities.
What’s the biggest threat facing Nigerian retail industry analysis today?
E-commerce represents the biggest disruptive threat, reshaping customer expectations and competitive dynamics. Additionally, economic volatility, currency instability, and infrastructure deficits pose ongoing challenges. Retailers who adapt to these threats while building strong customer relationships will thrive.
How often should businesses review their Porter’s Five Forces retail analysis?
Businesses should conduct comprehensive Porter’s Five Forces reviews annually, with quarterly updates for rapidly changing aspects. Major market shifts, regulatory changes, or competitive actions warrant immediate reassessment. Regular monitoring ensures strategies remain aligned with evolving market dynamics.
Why choose Novatia Consulting for retail strategy in Nigeria?
Novatia Consulting combines deep understanding of Nigerian retail industry analysis with proven strategic frameworks like Porter’s Five Forces. Our local expertise, practical implementation support, and commitment to client success deliver actionable strategies that create sustainable competitive advantages in retail market competition Nigeria.







